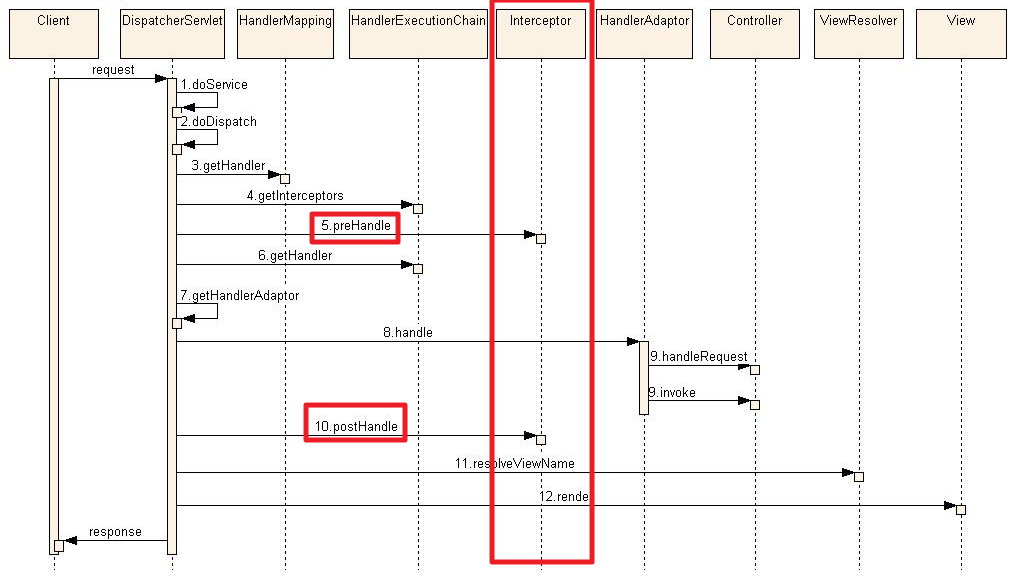
Interceptor
Interceptor는 "가로채다"라는 의미를 가지고 있다.
Spring에서도 해당 의미와 유사하게
Client에서 Server로 보낸 Request 객체를 Dispatcher Servlet의 Controller에 도달하기 전에 가로채는 역할을 한다.
Interceptor를 통해 가로챈 요청에 추가 로직을 넣을 수도 있고, Request 객체를 검증하는 작업도 할 수 있다.
Interceptor를 사용했을 때의 장점은 아래와 같다
- 공통 로직을 사용하는 경우 코드 누락에 대한 위험성 감수
- 코드 재사용성 증가
- 메모리 낭비, 서버 부하 감수
어떠한 프로그램이든 공통 로직은 한 곳에서 관리하는 게 가장 좋다.
그런 면에서 Interceptor는 좋은 옵션을 제공한다.
사용 예제
@Component
public class MyInterceptor implements HandlerInterceptor {
@Override
public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler)
throws Exception {
// do what you want ..
return true;
}
@Override
public void postHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler,
ModelAndView modelAndView) throws Exception {
// do what you want ..
}
@Override
public void afterCompletion(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response,
Object handler, Exception ex)
throws Exception {
// do what you want ..
}
}
Interceptor를 구현하기 위해서는 "HandlerInterceptor"를 Implements 받으면 된다.
해당 Interface에는 아래의 3가지 메서드를 제공한다.
- preHandler(...)
- Controller가 호출되기 전에 실행된다
- return 값은 boolean으로 해당 값이 false이면 Controller가 호출되지 않는다
- postHandler
- Controller가 호출 된 이후지만, View가 생성되기 전에 실행된다
- ModelAndView 객체를 인자로 받아 View를 생성하기 전에 해당 객체의 정보를 조작할 수 있다
- afterCompletion
- View의 모든 작업이 완료된 후에 호출된다
@Configuration
@RequiredArgsConstructor
public class WebConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer {
private final MyInterceptor interceptor;
@Override
public void addInterceptors(InterceptorRegistry registry) {
registry.addInterceptor(interceptor).addPathPatterns("/**");
}
}
작성한 Interceptor를 Spring에 등록하기 위해서는 WebMvcConfigurer를 Implements 하여서 코드를 추가해야 한다.
WebMvcConfigurer 해당 Interface에 addInterceptors라는 메서드에서 추가해 주면 된다.
또한 해당 Interceptor가 어떠한 조건일 때 실행되고, 실행되지 않는 등의 설정을 추가할 수 있다.
'Spring > etc' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Spring] @PreAuthorize, @PostAuthorize에서 Custom Security Expression 사용하기 (0) | 2021.11.27 |
|---|---|
| [Spring] Spring Security Annotation (@PreAuthorize, @PostAuthorize, @Secure) (0) | 2021.11.24 |
| [Spring] @WebMvcTest 작성 시 Spring Security 유의사항 (0) | 2021.09.29 |
| [Spring] Controller Layer Test 코드 작성 (+예시) (0) | 2021.09.09 |
| [Spring] 구동 시점 로직 추가 (CommandLineRunner ApplicationRunner) (0) | 2021.09.02 |